
Cancer can unfortunately develop for people of any age, at any time. As of 2020, there were more than 18.1 million cancer cases recorded across the globe. While various types of cancer can affect anyone, there are some types of cancer which appear more commonly among younger people.
In 2020, the American Cancer Society predicted there would be approximately 89,500 cancer cases, and 9,270 deaths among young adults between the ages of 15 to 39 throughout the US.
Although the majority of cancer cases are often diagnosed in people over the age of 65, certain types of cancer are statistically more present in those under the age of 45.
Knowing which types of cancer are more common among young adults can help you to be more vigilant when maintaining an awareness of potential signs and symptoms, particularly if you know you have a stronger genetic risk for certain types of cancer.
Cancer Cases Among Young Adults
For statistical purposes, most researchers exploring the common types of young adult cancer focus on people between the ages of 20 and 39. The more we study cancer, the more we learn that certain types are more likely to apply to different age groups.
In older people, cancers of the colon, rectum, skin, prostate, lung, and breast are most common. Cancers in older adults are often linked to lifestyle factors, such as not getting enough exercise, obesity, smoking, aging, unhealthy diet and other factors like exposure to chemicals. However, some are influenced by genetic mutations.
Cancers in children and teenagers are much less common, and often develop as a result of a genetic predisposition. Unlike cancers in older people, cancers in children are less likely to be a result of environmental or lifestyle factors.
Cancer cases among young adults can be a result of various factors, from genetic mutations to lifestyle and environmental influences. According to the latest research, among people in their 20s, the most common cancers include testicular, thyroid, and blood cancers (such as lymphoma).
For adults in their 30s, breast cancers and melanomas are more common.
Common Types of Cancer in Young Adults
The types of cancer most likely to affect young adults are not restricted to this age group of 20-39. Cancer can occur at any time of a person’s life. However, researchers say people between the ages of 15 and 39 are now reporting more cancer cases than ever before, particularly in regard to thyroid cancer.
Some of the most common cancers reported for people under the age of 45 include:
Brain and CNS Cancers
Brain and central nervous system cancers are the third most commonly occurring cancers among people aged 35-39. Brain tumors account for around 85-90% of all central nervous system cancers. Among children, these tumors typically start in the lower part of the brain, such as the brainstem or cerebellum. Whereas in adults, it’s more common to develop tumors in the upper parts of the brain.
The most common symptoms of brain and central nervous system cancers include persistent headaches, changes in speech, difficulty with memory, alterations in vision or mood, and balance problems. Some people also experience weakness or tingling in their extremities.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is most common among older women, however, approximately 7% of women with this condition are diagnosed before the age of 40. For younger women diagnosed with breast cancer, lifestyle factors such as obesity can be a big factor, alongside genetics.
Research suggests breast cancer is one of the most common conditions among adolescents, and young adults aged between 15 to 39 years. However, the survival rate for younger people tends to be better. For people with a family history of breast cancer, it’s often a good idea to seek out screening earlier than the general population, to catch issues early.
The most common signs of breast cancer include new lumps or masses in the breast. Other possible symptoms can include pain or swelling, changes to the nipple, fluid leaking from the nipple, and thickening or changes to the breast skin.

Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is most common in women between the ages of 35 and 44. Most of the time, cervical cancer can be found early, or prevented with the use of screening tests, and vaccinations against HPV – the virus most commonly connected to cervical cancer.
Patients with a genetic history of cervical cancer, or cancer in the female reproductive system should seek out screening at an early age. However, every woman should submit their sample to regular pap and HPV testing to prevent this issue. The most common symptom of this condition is abnormal vaginal bleeding, but some people also experience pain and discomfort during sex.
Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer is one of the most common types of cancer among younger men. Approximately half of all cases occur in men between the ages of 20 and 34. The average age for a diagnosis of testicular cancer today is 33. Fortunately, this is also one of the most curable forms of cancer.
Most often, the first symptoms of testicular cancer will include a lump within the testicle, or swelling around the testicles. Some tumors are painful, while others cause no sensation. It’s important for men of any age to have any presence of unusual growths checked.
Colorectal Cancer
Most people assume cancers of the rectum and colon are most common among older adults. However, researchers suggest the number of colorectal cancers among people between the ages of 15 and 39 are increasing. Incidence of colorectal cancer among people under the age of 50 has doubled since the 1990s. Some experts believe diet, lifestyle and environmental issues may be to blame.
Genetics are also a common factor in the development of colorectal cancers. Inherited conditions can increase a person’s risk, making screening more crucial. Many medical practices are beginning to encourage earlier screening for younger adults.
Symptoms of colorectal cancer can vary, but often include bleeding, changes in bowel habits, loss of appetite or weight, stomach pain, and dark-colored stools.
Lymphoma
Lymphomas are a form of cancer which occur within the lymphocyte immune cells. These cancers affect various lymph tissues and nodes, including the thymus and tonsils. They can also impact the bone marrow and various organs.
There are two main forms of lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin, and Hodgkin lymphoma. While Hodgkin lymphoma is less common overall, it’s one of the most common cancers in the young adult and adolescent population, aged 15 to 39. Around 30% of cases occur in patients between the age of 15 and 25.
Lymphomas can cause various symptoms depending on the location of the tumor, but common symptoms include weight loss, sweating, fever, tiredness, and swelling under the skin around the armpit, groin, or neck.
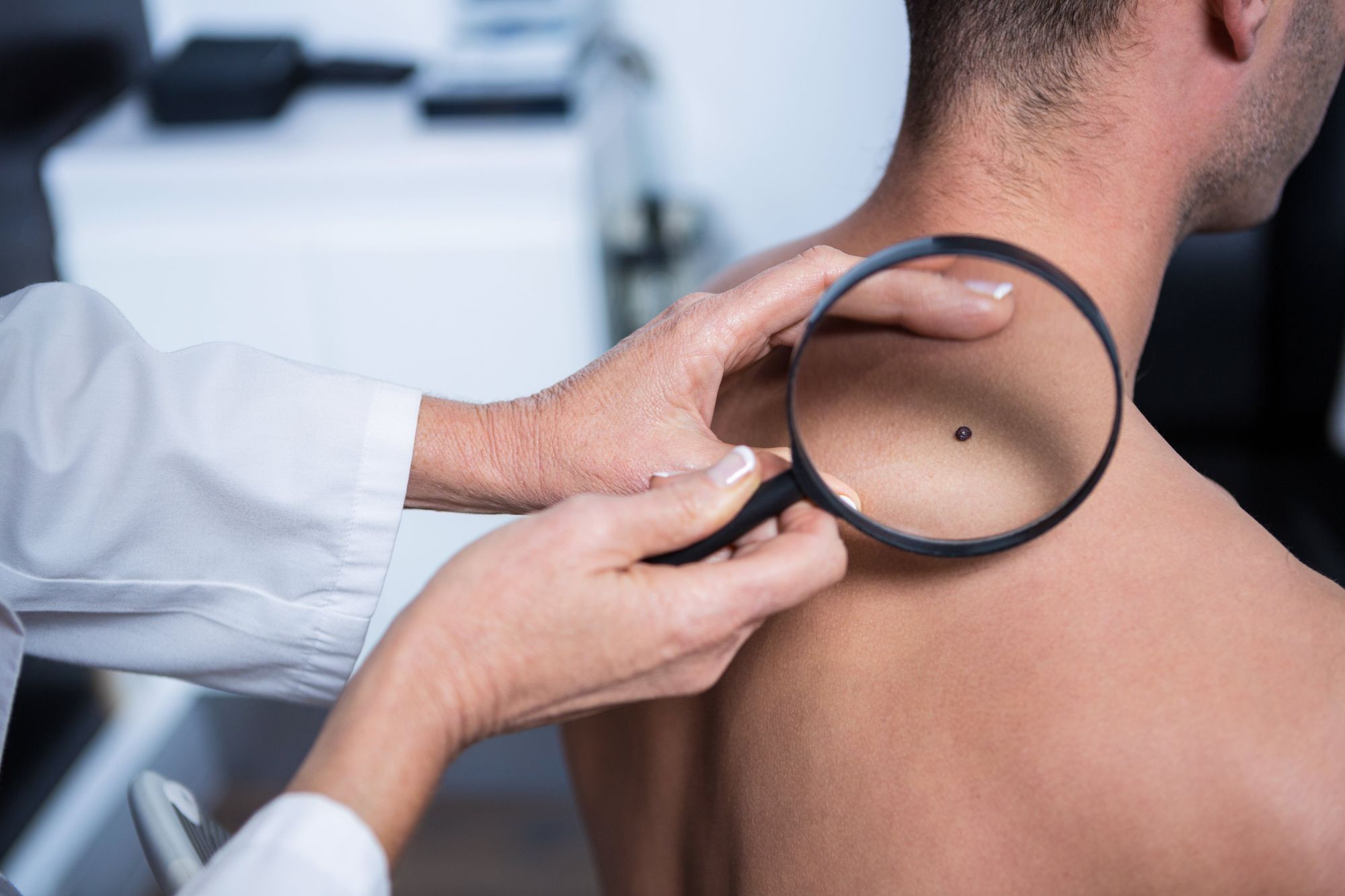
Melanoma (Skin Cancer)
Melanoma is a common type of skin cancer which can be particularly prominent among younger adults. In 2020, 2,400 cases of melanoma were reported by people aged between 15 and 29. The condition is particularly common among younger women. Melanoma affected by genetics can occur in patients at a much younger age.
The chances of treating melanoma are high when the condition is diagnosed early. The most common sign of this cancer is a new spot or mark on the skin, or a spot which changes in color, shape, or size. A mark on your skin which appears different to all other spots might be a warning.
Check out this helpful article about skin cancer prevention.
Sarcomas
Sarcomas are types of cancer which occur within the connective tissues of the body, such as fat cells, bones, and muscles. There are two main types of sarcomas: soft tissue, and bone sarcomas. Soft-tissue sarcomas account for around 8% of all tumors in young adults and adolescents.
Soft tissue sarcomas often cause symptoms such as lumps or swelling, bowel problems, and pain, depending on where the tumor is located. In bone sarcomas, symptoms are most likely to cause discomfort around the bones, particularly in the pelvic, chest, or shoulder area.
The two most common types of bone cancer, Ewing sarcoma and osteosarcoma are most common in teens, but they can also occur frequently in young adults.
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is more likely to occur as people get older. However, it is also one of the most common cancers found among adults of a younger age. Specifically, women are at a high risk of thyroid cancer. Around 3 times more women develop thyroid cancer than men.
Studies show the incidence of thyroid cancer among young adults is rising. However, the prognosis for most forms of this cancer is excellent when the issue is detected early. The most common symptom of thyroid cancer is the formation of swelling or lumps at the front of the neck. The condition may also cause respiratory problems, swallowing issues, and changes in your voice.
The Rising Threat of Cancer for Young Adults
Cancers can occur at any age, as the result of various factors, from diet, lifestyle and environmental issues to your DNA. However, cancer diagnosis among younger adults is growing, which indicates how important it is for younger people to be aware of signs and symptoms, and think about prevention.
While your chances of treating any of the cancers mentioned above is better at an early age, it’s very important to find and treat the issue as early as possible. If you’re aware of a genetic predisposition to certain types of cancer, and you notice the symptoms of a specific cancer, it’s important to notify your doctor, and be your own advocate. Don’t let your doctor brush you off, and instead, ask for the proper scans and cancer screenings.
Remember that cancer symptoms can be subtle, so always use professional medical advice to investigate symptoms, even if it’s a symptom as subtle as an odd color of urine.
Prevention is better than hope for a cure, so it’s helpful to find out if you have any cancer-causing genetic mutations. If you do, this doesn’t mean you’ll for sure get cancer, but this information can prompt you to take preventative lifestyle measures and frequent medical screenings. You can find out your genetic cancer and disease risk by taking a DNA test from CircleDNA.







Comments are closed.