
Introduction:
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, or PCOS, is a prevalent hormonal disorder that affects roughly 1 in 10 women in their reproductive years. It is characterized by a range of symptoms and hormonal imbalances that can have significant impacts on a woman’s health and well-being, even increasing the risks of various diseases.
Unfortunately, many women tend to discover that they have PCOS when trying to conceive. Despite the telltale signs, an alarming 75% of women do not receive a timely diagnosis, and ultimately suffer from fertility issues. It’s especially demoralizing because in those cases, early detection could have helped with those trying to conceive.
But rather than pointing fingers, we can better face this widespread disorder by being aware. Knowing the causes, symptoms, effects, and other variables tied to PCOS will help you be more proactive and prevent any potential consequences.
Causes of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome:
So what causes PCOS in the first place, and how does it come about? While the exact cause of PCOS remains unclear, it is believed to be a complex condition influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Several key factors contribute to the development of PCOS:
- Hormonal Imbalances: PCOS is characterized by an imbalance in sex hormones, particularly an excess production of androgens (male hormones) such as testosterone. This hormonal imbalance disrupts the normal functioning of the ovaries, leading to the formation of cysts and irregular ovulation.
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin is a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. In women with PCOS, their cells become less responsive to insulin, resulting in insulin resistance. This can lead to higher insulin levels in the blood, triggering the ovaries to produce more androgens and interfering with normal ovarian function. Insulin resistance also contributes to the accumulation of visceral fat, which further exacerbates the hormonal imbalances and increases the risk of metabolic disorders.
- Genetic Factors: There is evidence suggesting a genetic component to PCOS. Women with a family history of PCOS are more likely to develop the condition themselves, indicating a genetic predisposition. Specific gene variations and mutations related to hormone regulation and insulin signaling have been identified as potential contributors to PCOS development.
- Lifestyle Factors: While genetics play a role, lifestyle factors can also contribute to the development and severity of PCOS. Poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and obesity are associated with an increased risk of PCOS. Excess body weight can exacerbate insulin resistance and hormone imbalances, making the symptoms of PCOS more pronounced.

Common Symptoms Experienced by Women:
PCOS can manifest in various ways, and the intensity and variety of symptoms often vary from woman to woman. However, some of the most common symptoms include:
- Irregular Menstrual Cycle: Women with PCOS often experience irregular or infrequent menstrual cycles, or may even experience complete absence of menstruation (amenorrhea).
- Excessive Hair Growth: Due to the elevated levels of androgens, women with PCOS may develop excess hair growth on the face, chest, abdomen, and other areas typically associated with male-pattern hair growth (hirsutism). This can especially be taxing on a woman’s self-confidence.
- Acne and Oily Skin: Hormonal imbalances in PCOS can lead to increased sebum production, resulting in acne breakouts and oily skin.
- Weight Gain: Many women with PCOS struggle with weight management, as the condition can disrupt metabolism and make it easier to gain weight. The struggles with weight management can lead to low self-esteem, body image issues, and an increased risk of developing other health problems such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
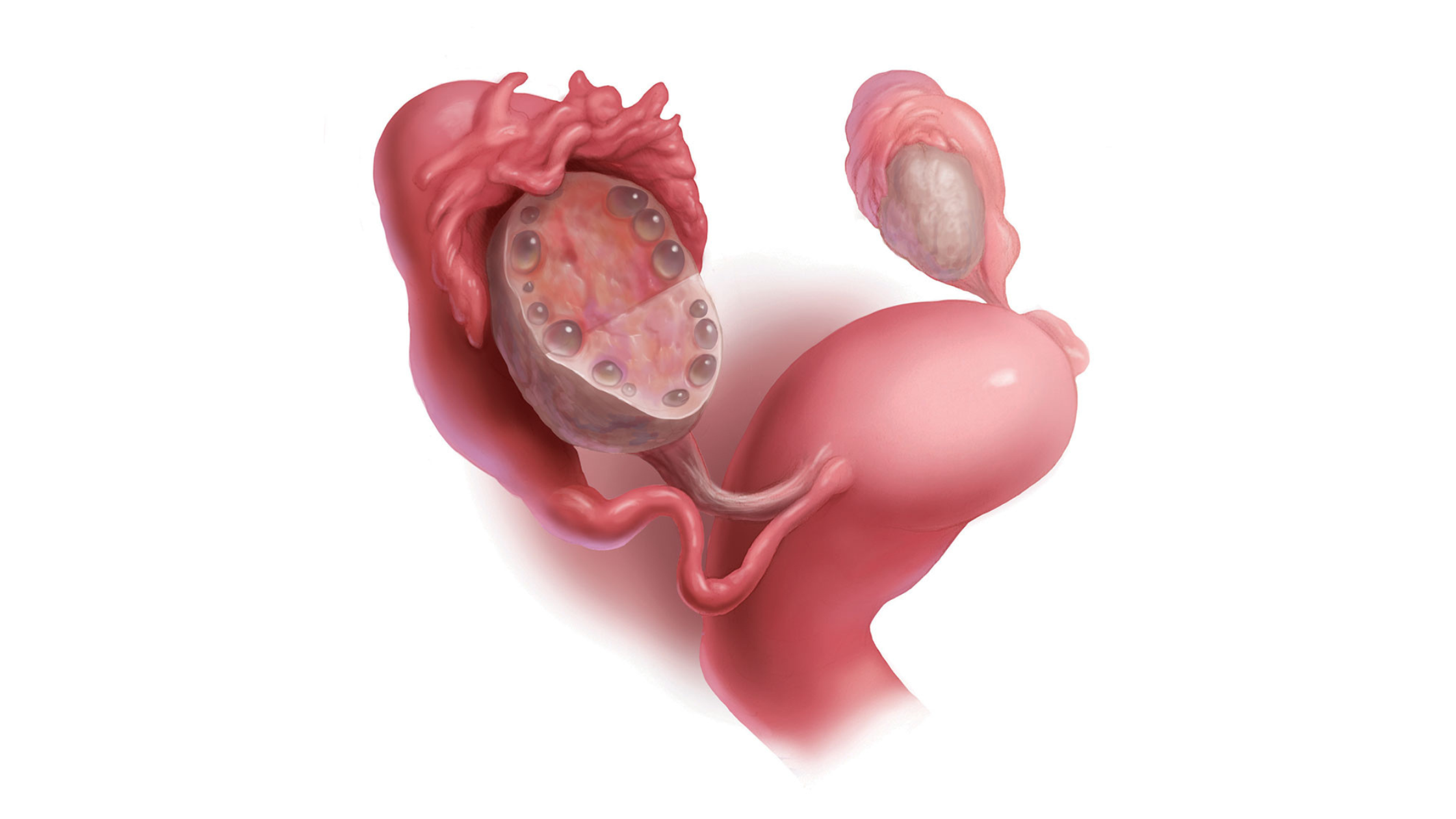
- Polycystic Ovaries: One of the defining features of PCOS is the presence of enlarged ovaries with small cysts. However, it is important to note that not all women with PCOS have visible cysts, and some women without PCOS may have ovarian cysts. On their own, ovarian cysts aren’t particularly dangerous, but they can be harmful when ruptured or twisted.
The Importance of Early Detection in PCOS Diagnosis
The thought of PCOS and its consequences can be scary, but it doesn’t have to be.
Early detection of PCOS is crucial for several reasons, as it allows for timely intervention, management of symptoms, and prevention of potential long-term health risks. Detecting PCOS in its early stages empowers women to take proactive steps towards their health and well-being.
Firstly, early detection enables healthcare professionals to initiate appropriate treatment strategies promptly. PCOS is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. By identifying PCOS early, healthcare providers can help women understand the condition, its impact on their health, and the available treatment options. Early treatment interventions can help regulate menstrual cycles, manage symptoms such as hirsutism and acne, and minimize the risk of associated health complications.
Secondly, early detection of PCOS is crucial for women who are planning to start a family. PCOS is a leading cause of female infertility, as it often disrupts ovulation and affects reproductive function. Detecting PCOS early allows women to seek fertility treatments and interventions at an earlier stage, increasing their chances of conception and successful pregnancy.
Furthermore, early detection can help prevent or manage long-term health risks associated with PCOS. Women with PCOS are at a higher risk of developing insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, and endometrial cancer. By identifying PCOS early, healthcare providers can implement preventive measures, such as lifestyle modifications, medications, and regular health screenings, to mitigate these risks and promote overall health.
Lastly, early detection of PCOS provides women with knowledge and understanding of their condition. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health, seek appropriate medical care, and adopt lifestyle changes that can positively impact their well-being.
So how do you go about making the first move against PCOS? With a genetic test like CircleDNA’s very own comprehensive kits, you can reveal insights on your genetic factors that may contribute to PCOS development, right from home. From understanding how to diet according to your body’s unique requirements to understanding your genetic risks for certain diseases, you are the one in charge of your long term health, including preventing PCOS.
